COVID-19 has wreaked havoc on our health systems, the economy, and our families. For families in the midst of a divorce, the stress and anxiety you would normally experience during this time are even more amplified. Recently, Congress adopted the CARES Act, which is designed to help families navigate the financial pressures we are all facing during this time. Over the last several days, the Savannah divorce lawyers at Johnson Kraeuter, LLC, have been researching the various components of the Act and consulting with financial professionals to provide you with the most accurate information possible. Much of the information contained in this post has been provided by Brad Whitfield of Coastal Consulting Management Group and Sherri Holder of The Holder Group. If you have questions about specific financial decisions, we encourage you to contact either of them for more information.
If you are in the midst of a divorce, here is what you should know about how the Act impacts your situation.
BENEFITS FOR FAMILIES
Stimulus Checks
Individuals with income below $99,000 per year, and families with income below $198,000 per year can expect to receive a stimulus check in some amount. The amount you receive depends on your income and household.
- Individuals earning $75,000 or less will receive $1,200. Individuals who earn between $76,000 and $99,000 will receive a check-in some amount lower than $1,200.
- Married couples earning $150,000 or less will $2,400, while those who earn between $151,000 and $198,000 will receive some amount lower than $2,400.
- For each child under 16 in the household, families will receive an additional $500.
- Taxpayers filing as head of household will receive $1,200 if they earn $112,500 or less.
Your income will be assessed based on your 2019 tax return. If you have not filed your 2019 tax return, it will be based on your 2018 tax return. If you are not typically required to file taxes, you may have to file a simple return for 2019 in order to receive your stimulus. If you have provided a bank account for direct deposit in your tax returns, your stimulus should be deposited directly to your account.
Potential issues:
- Joint Accounts: If you and your spouse filed joint taxes and provided joint account information for a direct deposit, the stimulus will likely be deposited into that joint account. Neither party should spend this money unilaterally or without the opposing party’s knowledge and consent.
- Individual Accounts: If you filed jointly but designated an individual account for direct deposits of tax refunds, that stimulus will likely be deposited into that individual account. That does not mean that the stimulus deposit is separate property, and the party receiving the deposit should not spend it without the opposing party’s knowledge and consent.
- Checks: If you have not designated any account for direct deposits, you may receive a check. The check will be mailed to the address that you designated on your most recently filed tax return. If you filed jointly, the check will likely be made out to you and your estranged spouse jointly. Neither party should deposit the check unilaterally or spend the money without the opposing party’s knowledge and consent.
*************
If you think you are entitled to receive a stimulus, contact your Savannah attorney right away so that your attorney can negotiate with opposing counsel to reach an agreement about how the stimulus funds will be allocated between the divorcing couple. It is risky for either party to unilaterally spend that money without an agreement from the other party.
*************
Mortgage Forbearance
The CARES Act does not require mortgage companies to forbear mortgage payments, but many mortgage companies are offering forbearance to individuals negatively impacted by COVID-19. Each company has a different process, so you should contact your individual mortgage lender to learn details. It is imperative you tell the mortgage company you are negatively impacted by COVID-19 in order to learn the full range of options available to you.
Potential issues:
- Property rights: Forbearance could potentially impact the Parties’ property rights by making the property more vulnerable to foreclosure in the future.
- Marital Assets: Forbearance could potentially impact the value of the property and thereby decrease the value of the marital assets as a whole.
- Marital Debt: Forbearance could potentially increase the marital debt.
- Credit Scores: Forbearance could potentially impact the Parties’ credit scores.
- Court Order: If you are required to pay a mortgage pursuant to a temporary or final court order, forbearance does not suspend your obligations to make these payments. Likewise, if your ex-spouse or spouse is responsible for making your mortgage payments, forbearance does not suspend that obligation.
*************
Contact your attorneys in Savannah GA right away if you need mortgage relief so your attorney can negotiate an agreement about the best way to seek mortgage relief while protecting the marital estate and insuring compliance with court orders. Neither Party should unilaterally forbear a mortgage without the knowledge and consent of the other Party.
*************
Student Loans
Government-backed student loans are automatically in forbearance until September. Any auto-debit payments should be suspended automatically during this time. Additionally, businesses are incentivized to pay up to $5,250 for each employee. These payments would be exempt from income taxation for employees, and employers receive certain benefits of treating the payment like wages.
Potential issues:
- Court Orders: If you pay your spouse’s or your ex-spouse’s student loans pursuant to a court order, CARES does not suspend your obligations to make these payments. Likewise, if your ex-spouse or spouse is responsible for making your student loan payments, CARES does not suspend that obligation.
- Income: Child support and alimony are calculated based on your income. Accepting the benefit of a student loan payment by your employer could increase your income in such a way that it increases your child support and alimony obligations.
- Marital Debts: Forbearing student loans could potentially decrease the value of the marital estate because student loan debt is not being reduced during the forbearance period.
*************
Contact your attorney right away if you have student loan debt or are responsible for paying your spouse’s or ex-spouse’s student loan debt. Your attorney can negotiate an agreement about the best way to manage student loans while protecting the marital estate. Neither Party should unilaterally forbear a student loan or accept student loan payments from an employer without the knowledge and consent of the other Party.
*************
Retirement Accounts
Up to $100,000 can be withdrawn from a retirement account without paying the usual 10% penalty and enjoying a 3-year repayment period. Possible issues:
Potential issues:
- Marital Assets: Depleting retirement accounts depletes the value of the marital estate. In many cases, the court may have restrained both parties from withdrawing funds from accounts, including retirement accounts. It is important that you do not violate a restraining order by withdrawing funds without the other party’s knowledge and consent.
- Marital Debts: Because the loans must be repaid within three years, withdrawing retirement funds under this scheme increases the marital debts.
*************
Contact your attorney right away if you plan to withdraw retirement funds under this scheme. Your attorney can negotiate an agreement about the best way to protect the marital estate. Neither Party should unilaterally deplete retirement accounts without the knowledge and consent of the other Party.
*************
BENEFITS FOR SMALL BUSINESSES AND THE UNEMPLOYED
A summary of the CARES Act provisions is provided below. For more details, consult The Small Business Owner’s Guide to the CARES Act.
Unemployment
Unemployment benefits have been expanded to increase the amount individuals receive and the length of time unemployed individuals are eligible to receive benefits. Independent contractors and the self-employed are now also eligible for unemployment benefits.
Loans and Grants
A number of loans and grants have been approved in the CARES Act. The following table is a concise summary of the primary options available:
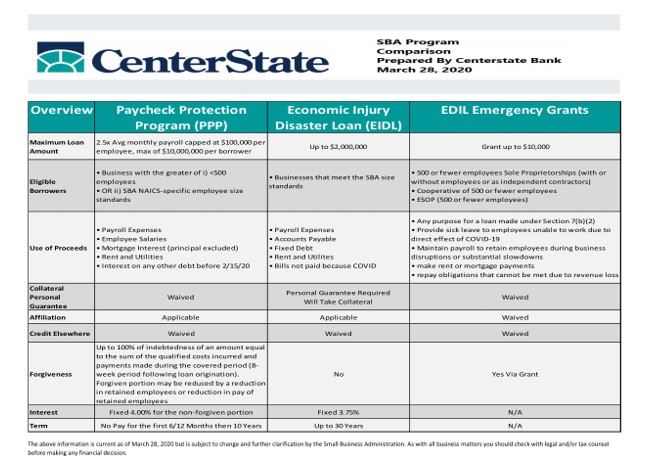
Things to keep in mind:
- There are limits on how much money is available, so apply soon.
- There are conditions on how you qualify for this money and how you spend this money.
- You will need to keep meticulous records of how you spend this money.
- Some of this money is in the form of a forgivable loan, while some will require repayment with interest over time.
- The Paycheck Protection Program will be administered through banks and backed by the SBA. The best way to claim this benefit is to work with a bank with whom you already have a relationship.
- EIDL Loans and Grants are administered directly through the SBA.
- For more information on how to apply, check out the Applications for Small Business Paycheck Protection Program open April 3 published by the Journal of Accountancy and the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) Information Sheet. Here is a link to the Application for the Payroll Protection Program.
FMLA
CARES requires employers to pay sick employees two weeks of paid sick leave with ten weeks of expanded FMLA benefits after that. Employers with less than 50 employees are required to provide 10 additional sick leave days to employees. Employers will receive tax credits if they have not opted for the Payroll Protection Program.
Government Contractors
Governmental agencies will be able to modify the terms and conditions of a contract and reimburse contractors at a billing rate of up to 40 hours per week of any paid leave, including sick leave.
Payroll
Employers can claim an employee retention credit of 50% of wages up to $10,000. Employers can also defer paying the employer portion of certain payroll taxes through the end of 2020, with all 2020 deferred amounts due in two equal installments, one at the end of 2021, the other at the end of 2022. Payroll taxes that can be deferred include the employer portion of FICA taxes, the employer and employee representative portion of Railroad Retirement taxes (that are attributable to the employer FICA rate), and half of SECA tax liability. Employers receiving Payroll Protection Program loans are not eligible to claim any of these credits.
Bonus Depreciation
CARES permits retroactive bonus depreciation for Qualified Improvement Property for tax years 2017 and 2018. It includes a provision to treat the 39-year like a 15-year. Claiming this bonus depreciation requires filing an amended tax return.
Debt Relief
Some SBA loans are eligible for debt relief, in particular loans provided under 7(a) and 504, as well as microloans. This provision requires the SBA to cover all loan payments on these SBA loans, including principal, interest, and fees, for six months.
Minimum Distribution
Required minimum distributions are suspended for 2020.
Charitable Deductions
The limit on charitable deductions has been suspended in 2020.
Student Loan Payments
Employer payments of employees’ student loans up to $5,250 are non-taxable.
Bankruptcy
Businesses that are currently in bankruptcy are likely not eligible for relief under CARES.
For more personalized guidance on how to navigate your divorce during a pandemic, contact Johnson Kraeuter, LLC, today.

